Using GBIF-mediated data
|
In this module, you will learn how GBIF’s data is used and accessed. |
| This is a review of information found in the Introduction to GBIF course, if you need a refresher. |
How is GBIF-mediated data used?
The GBIF literature tracking system has identified over 10,000 uses (July 2024) of GBIF mediated data, most of which are in peer-reviewed articles. The majority of these uses are in the field of ecology, but others relate to climate change, conservation, human health and agriculture. A systematic review of the use of GBIF-mediated data by Heberling et al. (2020) showed:
-
Both data availability and data use have increased over time.
-
Data integration facilitates global research and access.
-
Uses of GBIF-mediated data span disciplinary boundaries.
-
The scientific areas using GBIF-mediated data are conceptually diverse and change in prevalence over time.
-
Globally integrated datasets enable researchers to ask both basic and applied questions at taxonomic, temporal and spatial scales that would be otherwise impossible.
-
The synergistic roles of observation- and specimen-based biodiversity data highlight the value and need for deeper integration with phylogenetic, environmental, phenotypic, ecological and genetic sources of data.
GBIF-mediated data is also used for monitoring the state of biodiversity and progress towards achieving the targets of the Convention on Biological Diversity. The increase in availability of GBIF occurrence data is one of the indicators for tracking progress towards the achievement of Aichi Biodiversity target 19 and GBIF is a key data source in the creation of a number of other indicators, including the Species Status Information Index, Species Habitat Index and the Biodiversity Habitat Index.
While the utility of GBIF-mediated data is clear, the wide variety of sources of data accessible through GBIF, spanning museum collections, citizen science, metagenomics, among others, means that not all GBIF-mediated data will be fit for every use. Key components of using GBIF-mediated data are understanding how to access the specific data that you need from what is available in GBIF and understanding some of the common data quality issues that affect the data so as to facilitate processing of the data before analysis.
How is GBIF-mediated data accessed?
There are two main points of access to GBIF-mediated data: GBIF.org and the Application Programming Interface (API) services. Using the website requires no programming experience and allows for quick and easy search, filter and download functions for GBIF-mediated data, as well as a range of additional tools and metrics that are not available through API services. API services allow continued access to GBIF-mediated data through other systems and can be the basis for the development of tools that allow for the interrogation of the data. Examples include a number of R packages, such as rgbif and CoordinateCleaner, as well as more specialized tools that allow for more specific use cases, such as GeoCat for Red List assessments.
What is available to me?
Through the search functions on the website, users can access data that can either be directly downloaded through GBIF or accessed from the original sources following links that GBIF provides.
| Remember that as a data user you should read and agree with the terms of the GBIF Data User Agreement that include correctly citing the use of GBIF-mediated data. |
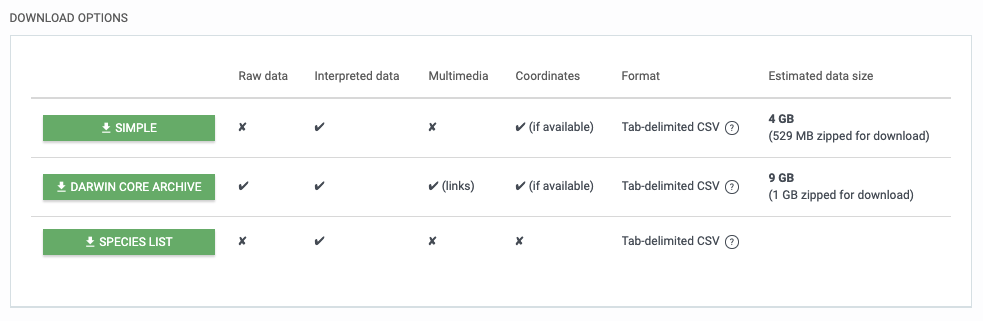
The data available to you are:
-
Primary biodiversity data - occurrence, checklist and sampling event data that is provided to users through the one of the 3 download formats:
-
Simple: Tab delimited CSV. Only contains the data after GBIF interpretation. No multimedia included.
-
Darwin Core Archive: The Darwin Core Archive (DwC-A) contains both the original data as the publisher provided it and the GBIF interpretation. Links (but not files) to multimedia included.
-
Species list: Tab delimited CSV with the distinct list of names in the search result and as a map visualization of the data.
-
-
A range of metrics are provided for countries and regions, data publishers, datasets and data searches that provide taxonomic breakdowns, trends in data collection and highlight data quality issues. For countries, these metrics can be also be downloaded in the form of a PDF activity report.
-
Searchable database of publications that have used GBIF-mediated data.
Searches can be performed on the occurrences, species, datasets, publishers and resources, and each search function carries a set of filters that allow for more refined searching and additional data associated with the data, for example, images, can be found in tabs associated with the search.